In contrast the instantaneous values of the current voltage and resulted power in an AC circuit are continually changing by the supply. The current waveform distortion that contributes to reduced power factor is caused by voltage waveform distortion and overheating in the neutral cables of three-phase systems.

The Sine Wave Explained Ac Waveform Analysis Youtube
Linear Time-Varying Oscillators are time-varying systems since.

. The DC-link quantity is then impressed by an energy storage element that is common to both stages which is a capacitor C for the voltage DC-link or. RMS Value of sinusoidal AC current is. The DC output of the battery is bucked or boosted according to the requirement and then converted into AC using a DC-AC inverter.
Where necessary equipment manufacturers should specify the RCD Type required. A sine wave sinusoidal wave or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the sine trigonometric function of which it is the graphIt is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic functionIt occurs often in mathematics as well as in physics engineering signal processing and many other fields. The Type of RCD will depend on the characteristics of the equipment.
Unlike the series resonance circuit the resistor in a parallel resonance circuit has a damping effect on the circuits. The RMS voltage of a sinusoidal waveform can be obtained by multiplying peak to peak voltage with 122. Type AC devices can detect and respond to AC sinusoidal wave current.
Determine the time period T of waveform. The function of an inverter is to change a dc input voltage to a symmetric ac output voltage of desired magnitude and frequency. The stray-loss factor for copper conductors varies as the square of the load current and the square of the frequency and will therefore vary with the harmonic mix in the power supply.
Although the percentage contribution to distortion by higher harmonics decreases as the harmonic frequency rises its heating effect even if the harmonic. But what would happen to the characteristics of the circuit if a supply voltage of fixed amplitude but of different frequencies was applied to the circuit. Aluminum Conductor Characteristics.
For our example we will put T 2π and fx I m Sinωt in the formula. Because Phase Angle is often calculated from the fundamental component of each waveform distortion of either or both signals can result in mistakes the magnitude of which varies. Voltage and Current - The alternating current In an AC circuit is generated by a sinusoidal voltage source.
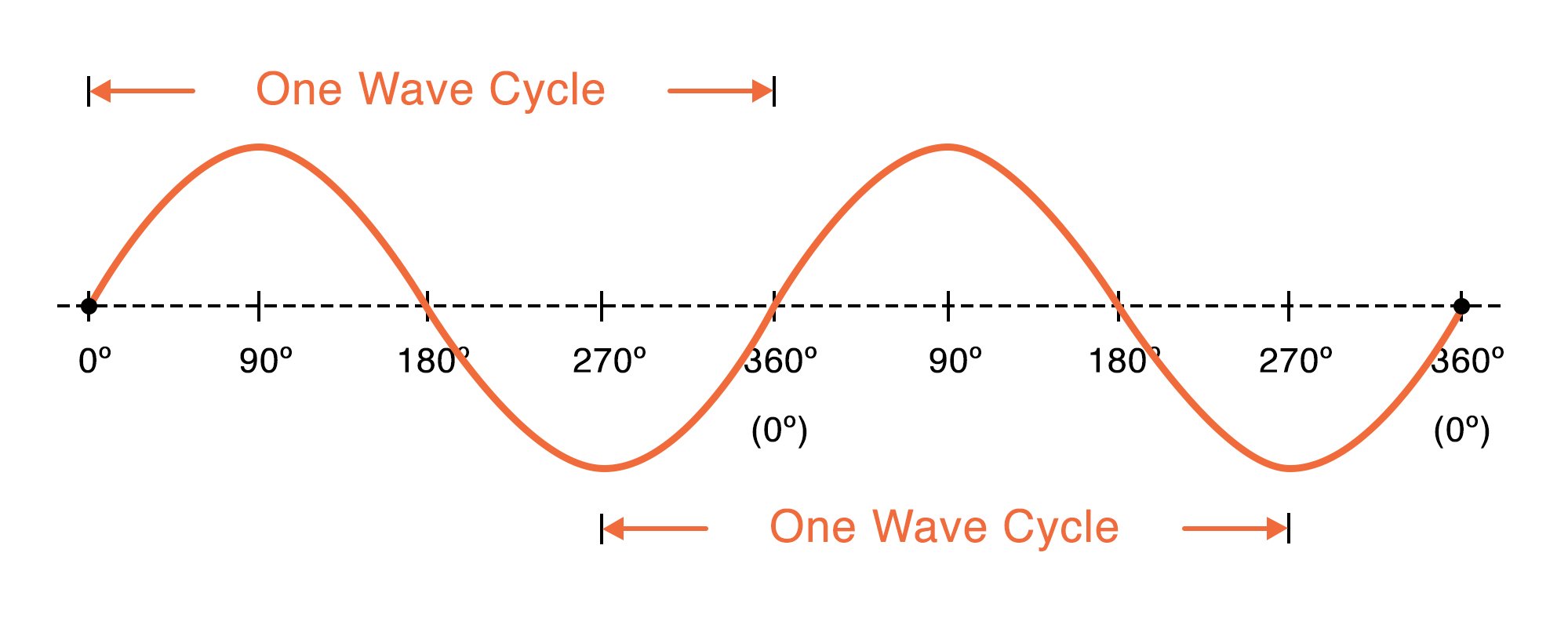
This demonstrates how the shape of the waveform is affected on various types of circuits under load and fault conditions. The overall pattern of positive vs. Representing phase in degrees treats one cycle of the waveform as a circle.
The dc power input to the inverter is obtained from an existing power supply network or from a rotating alternator through a rectifier or a battery fuel cell photovoltaic array or magneto hydrodynamic generator. Electrical Power in an AC Circuit. In DC circuits the voltages and currents are constant and do not vary with time as there is no sinusoidal waveform function related to the supply.
Its steady-state is a time-varying waveform periodic Its response to external noises varies with time 1 20 1 2 14 A. Cation of the AC line. Note that if the parallel circuits impedance is at its maximum at resonance then consequently the circuits admittance must be at its minimum and one of the characteristics of a parallel resonance circuit is that admittance is very low limiting the circuits current.
10 μV 025 of reading B grade Wide dynamic input range 100 μV rms to 3 V rms 85 V p-p full-scale input range Larger inputs with external scaling Wide bandwidth. 1 MHz for 3 dB 300 mV 65 kHz for additional 1 error. The output voltage waveforms of ideal inverters should be sinusoidal.
The inverter then changes the fixed voltage DC power to AC output power with adjustable voltage and frequency. We have also seen in our tutorial about series RLC circuits that two or more sinusoidal signals can be combined using phasors providing that they have the same frequency supply. An AC-AC converter with approximately sinusoidal input currents and bidirectional power flow can be realized by coupling a pulse-width modulation PWM rectifier and a PWM inverter to the DC-link.
The output waveform consists of a series of rectangular pulses with a fixed height and adjustable width. An op-amp detector that has the ability to detect the change from positive to negative or negative to a positive level of a sinusoidal waveform is known as a zero crossing detectorMore specifically we can say that it detects the zero crossing of the applied ac signal. Negative pulses is adjust-ed to control the output frequency.
Delivers true rms or average rectified value of ac waveform Fast settling at all input levels Accuracy. The dc-ac converter also known as the inverter converts dc power to ac power at desired output voltage and frequency. The phase difference between two sinusoidal waveforms of the same frequency and without a dc component can be easily represented as illustrated in the diagram.
For example a waveform that begins at zero displacement and shows its initial movement upward has a phase of 0o a waveform that begins at maximum positive displacement and shows its initial movement downward has a phase of 90o and so on. The RMS voltage of a periodic waveform or alternating waveform is given as Vrms Vavg x π 22 Vavg 11107. It is basically a voltage comparator whose output changes when the input signal crosses the.
Vrms Vp-px 1 22 Vp-px 0353. That is one cycle equals 360o. The time period T of the waveform is 2π as evident from its waveform.
Lee A General Theory of Phase Noise in Electrical Oscillators IEEE JSSC Feb.

Ac Waveform And Ac Circuit Theory Of Sinusoids

Ac Waveform And Ac Circuit Theory Of Sinusoids
Characteristics Of Sinusoidal Signals Sine Waves Video Tutorial
0 Comments